Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Ann Occup Environ Med > Volume 30; 2018 > Article
- Research Article The association between long working hours and work-related musculoskeletal symptoms of Korean wage workers: data from the fourth Korean working conditions survey (a cross-sectional study)
- Jae-Gwang Lee, Guang Hwi Kim, Sung Won Jung, Sang Woo Kim, June-Hee Lee, Kyung-Jae Lee
-
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 2018;30:67.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40557-018-0278-0
Published online: December 3, 2018
Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea
© The Author(s). 2018
Open AccessThis article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Reducing musculoskeletal disorders to enhance task performance among BPO workers: a partial least square structural equation modeling approach
Ma. Janice J. Gumasing
Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science.2026; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Musculoskeletal Symptoms and Associated Factors Among Iron Foundry Workers
Sibel Sert, Sevda Sungur, Mediha Bal, Selma Metintaş, Muhammed Fatih Önsüz
Workplace Health & Safety.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of prevalence and risk factors of musculoskeletal disorders among tea harvesting farmers: A systematic review
Bahram Kouhnavard, Mojtaba Khosravi Danesh, Mansour Shamsipour, Adel Mazloumi
WORK: A Journal of Prevention, Assessment & Rehabilitation.2025; 80(1): 10. CrossRef - The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Desktop Workers: Exploring the Link between Sleep Quality, Physical Activity, and Sedentary Lifestyles—A Cross-sectional Study
Manjarika Raj, Feba Roy
Journal of Society of Indian Physiotherapists.2025; 9(1): 47. CrossRef - Proactive Approaches to Work-Related Musculoskeletal Injuries in an Aging Workforce
Nimisha Kalia, Edward J. Bernacki, Xuguang (Grant) Tao
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2025; 67(2): e136. CrossRef - Commuting time and musculoskeletal pain in the relationship with working time: a cross-sectional study
Hoje Ryu, Seong-Sik Cho, Jung Il Kim, Sun-Haeng Choi, Nathan Kim
Ann Occup Environ Med.2025; 37: e4. CrossRef - Prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal complaints among surgeons in Saudi Arabia
Ahmed Saad Al Zomia, Tariq Ali Al Mufarrih, Asmaa Saad Habbash, Abdulrahman Saeed Alshahrani, Iffat Elbarazi, Abdulrahman Mohammed Almofareh, Mosab Abdulaziz Deajim, Rayan Mohammed Alshehri, Salaheddine Bendak, Abdulrhman Mohammed Alqarni, Faisal M Faye,
International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics.2025; 31(4): 1025. CrossRef - Prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal disorder and its associated factors among weavers in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abebe Kassa Geto, Chala Daba, Belay Desye, Gete Berihun, Leykun Berhanu
BMJ Open.2025; 15(8): e093124. CrossRef - Prevalence of low back pain and its associated factors among weavers in low- and middle- income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abebe Kassa Geto, Leykun Berhanu, Gete Berihun, Chala Daba, Belay Desye
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tipping the scales: how paid work hours thresholds impact health and gender wage disparities
Sunjin Pak, Amit Kramer, Yun-Kyoung Kim
The International Journal of Human Resource Management.2025; 36(13): 2342. CrossRef - Unraveling the after-hours dilemma: Consequences of overworking among teleworkers—A scoping review protocol
Bao-Zhu Stephanie Long, Kishana Balakrishnar, Luke A. Fiorini, Aaron Howe, Ali Bani-Fatemi, Basem Gohar, Behdin Nowrouzi-Kia, Marcos de Moraes Sousa
PLOS One.2025; 20(8): e0330594. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a six-month workplace therapeutic micro-exercise program on musculoskeletal pain: Initial anamnestic risk screening via TACOS and outcome evaluation using the Nordic Questionnaire
Mojtaba Ebrahimi varkiani, Amirhossein Vaghari gargari, Siavash Torkashvand
Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies.2025; 45: 365. CrossRef - The Hidden Cost of Long Working Hours: Occupational Anxiety and Argumentativeness in Emergency Nurses
Gürkan Özden, Ahmet Ceviz, Bahar Aslan, Muhammed Gönültaş
Journal of Emergency Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and evaluation of pattern of work-related musculoskeletal disorders among aluminum workers
Muhammad Audu Dan Inu, Mahmud Ali Karaga, Ibrahim Ahmad Abubakar, Abubakar Baba Saleh
Adesh University Journal of Medical Sciences & Research.2025; 7: 110. CrossRef - Assessment of the musculoskeletal discomfort scale for upper limb among workers in inner Brazil
Lara Karine Dias Silva, Alline Thamyres Claudino da Silva, Camyla Ferreira Moreno, Eloyse Ricely Machado de Souza, Tamires Fernanda Barbosa Nunes, Larissa Ane Hora de Souza, Lizandra Garcia Lupi Vergara, Jonhatan Magno Norte da Silva, Karen Jacobs, Remko
Work.2024; 78(1): 83. CrossRef - Study of musculoskeletal disorders risk factors and discomfort in sculptors in the north of Mexico
Patricia Eugenia Sortillón-González, Aidé Aracely Maldonado-Macías, David Saénz-Zamarrón, Juan Luis Hernandez-Arellano, Enrique Javier De la Vega-Bustillos, Karen Jacobs, Remko Soer
Work.2024; 78(1): 55. CrossRef - ‘Wait…, let me tell you, if I worked for a boss, I would be on sick leave': A Qualitative Study of Self-Employed Workers in Physically Demanding Jobs in the Netherlands
Bart Cillekens, Judith M. Mollet, Rixt A. Smit, P. Paul F. M. Kuijer, Pieter Coenen
Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation.2024; 34(3): 644. CrossRef - Biomechanical risk factors and subacromial pain provocation in healthy manufacturing workers
Claudio Muñoz-Poblete, Jaqueline Inostroza, Juan Carranza-Leiva
International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics.2024; 30(4): 1031. CrossRef - Identification of effective factors in musculoskeletal disorders of tea harvesting workers: a qualitative study
Bahram Kouhnavard, Adel Mazlomi, - Mansour Shamsipour
Occupational Health Journal.2024; 20(2): 201. CrossRef - Using Ecological Momentary Assessment (EMA) to understand occupation from the perspective of the experiencing self: An illustrative example in workers with type 1 diabetes
Raymond Hernandez, Rebecca Aldrich, Stefan Schneider, Arthur A. Stone, Shawn C. Roll, Elizabeth A. Pyatak
Journal of Occupational Science.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Work-related musculoskeletal symptoms among Saudi radiologists: a cross-sectional multi-centre study
Magbool Alelyani, Moawia Gameraddin, Abdullah Mohammed A. Khushayl, Aljoharah M. Altowaijri, Maryam Ibrahim Qashqari, Fahad Ali Ahmed Alzahrani, Awadia Gareeballah
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between irregular working hours and work-related musculoskeletal pain: results from the 6th Korean Working Conditions Survey
Munyoung Yang, Jun-Pyo Myong, Jongin Lee, Min Young Park, Mo-Yeol Kang
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Longer working hours and musculoskeletal pain: a meta-analysis
Sohrab Amiri
International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics.2023; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - Prevalence and risk factors of work-related musculoskeletal disorders among emerging manufacturing workers in Beijing, China
Xiaowen Ding, Ziyi Guan, Nan Liu, Mingli Bi, Fang Ji, Huining Wang, Xueyan Zhang, Baolong Liu, Dongsheng Niu, Tian Lan, Tingting Xie, Jue Li, Tenglong Yan
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between adverse ergonomic factors and work-related musculoskeletal symptoms among medical staff in China: a cross-sectional study
Fei Liu, Ning Jia, Chuansha Wu, Jingzhi Sun, Gang Li, Huadong Zhang, Dongxia Li, Rugang Wang, Jing Liu, Tianlai Li, Jixiang Liu, Ruijie Ling, Zhongxu Wang
Ergonomics.2023; 66(12): 2212. CrossRef - An Additional Effect of Electro-Acupuncture on Unspecified Chronic Low Back Pain Among University Employees in Al-kharj, Saudi Arabia: A Randomized Controlled Study
Gopal Nambi, Saud M. Alrawaili
Acupuncture & Electro-Therapeutics Research: International Journal of Integrated Medicine.2023; 48(3): 185. CrossRef - Does an increase in working hours affect mortality risk? The relationship between working hours and mortality among the older population
Murat A. Mercan, Hande Barlin, Nazire Begen
Work.2022; 71(3): 625. CrossRef - Associations Between Workplace Violence, Mental Health, and Physical Health among Korean Workers: The Fifth Korean Working Conditions Survey
Hae Ran Kim
Workplace Health & Safety.2022; 70(3): 161. CrossRef - The incidence of work-related musculoskeletal pain among administrators in a South African university
L.M. Moraba, T.J. Ellapen, Y. Paul
African Journal for Physical Activity and Health Sciences (AJPHES).2022; 28(3): 218. CrossRef - The prevalence of MSDs and the associated risk factors in nurses of China
Liang Tang, Guozhen Wang, Wei Zhang, Jie Zhou
International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics.2022; 87: 103239. CrossRef - Effects of multiple risk factors on upper limb musculoskeletal disorders among workers in inner Brazil
Iris Lima da Silva, Eloyse Ricely Machado de Souza, Lara Karine Dias Silva, Alline Thamyres Claudino da Silva, Jonhatan Magno Norte da Silva
Work.2022; 72(3): 885. CrossRef - A Study on the Factors Influencing Overall Fatigue and Musculoskeletal Pains in Automobile Manufacturing Production Workers
Jun Won Kim, Byung Yong Jeong, Myoung Hwan Park
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(7): 3528. CrossRef - Prevalence and Factors Associated with Musculoskeletal Disorders among Thai Burley Tobacco Farmers
Amarin Kongtawelert, Bryan Buchholz, Dusit Sujitrarath, Wisanti Laohaudomchok, Pornpimol Kongtip, Susan Woskie
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(11): 6779. CrossRef - Effectiveness and response differences of a multidisciplinary workplace health promotion program for healthcare workers
Kai-Hung Cheng, Ning-Kuang Wu, Chao-Tung Chen, Chih-Yu Hsu, Yen-An Lin, John Jiin-Chyuan Luo, Li-Ang Lee, Hai-Hua Chuang
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of lower extremity musculoskeletal disorders among manufacturing workers: a cross-sectional study in China
Xu Jin, Yidan Dong, Fujiang Wang, Ping Jiang, Zhongbin Zhang, Lihua He, Mikael Forsman, Liyun Yang
BMJ Open.2022; 12(2): e054969. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Musculoskeletal Disorders among Regular and Special Education Teachers: A Narrative Review
Ahmad Asyraf Abdul Rahim, Mohammad Saffree Jeffree, Dayang Maryama Ag Daud, Nicholas Pang, Mohd Fazeli Sazali
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11704. CrossRef - Investigating the relationship between working time characteristics on musculoskeletal symptoms: a cross sectional study
Jennifer L Garza, Jacqueline M Ferguson, Alicia G Dugan, Ragan E Decker, Rick A Laguerre, Adekemi O Suleiman, Jennifer M Cavallari
Archives of Environmental & Occupational Health.2022; 77(2): 141. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Musculoskeletal Disorders in Office Workers
Priska Aulianingrum, Hendra Hendra
The Indonesian Journal of Occupational Safety and Health.2022; 11(SI): 68. CrossRef - Long working hours and risk of 50 health conditions and mortality outcomes: a multicohort study in four European countries
Jenni Ervasti, Jaana Pentti, Solja T. Nyberg, Martin J. Shipley, Constanze Leineweber, Jeppe K. Sørensen, Lars Alfredsson, Jakob B. Bjorner, Marianne Borritz, Hermann Burr, Anders Knutsson, Ida E.H. Madsen, Linda L. Magnusson Hanson, Tuula Oksanen, Jan H.
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe.2021; 11: 100212. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Musculoskeletal Disorders Among Female Readymade Garment Workers in Bangladesh: A Comparative Study Between OSH Compliant and Non-Compliant Factories
Mohammad Hayatun Nabi, Pornpimol Kongtip, Susan Woskie, Noppanun Nankongnab, Dusit Sujirarat, Suttinun Chantanakul
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2021; Volume 14: 1119. CrossRef - Influence of risk factors associated with musculoskeletal disorders on an inner population of northeastern Brazil
Deividson Sá Fernandes de Souza, Jonhatan Magno Norte da Silva, João Vítor de Oliveira Santos, Maria Sonaira Braz Alcântara, Manoel Gerônio Lino Torres
International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics.2021; 86: 103198. CrossRef - The Relationship of Grip and Pinch Strength to Musculoskeletal Disorders in Female Carpet Weavers in Southeastern Iran, 2019
Naser Hashemi Nejad, Mostafa Mohammadian, Ali Akbar Haghdoost, Esmail Charkhloo
Indian Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2021; 25(3): 138. CrossRef - The relationship between chronotypes and musculoskeletal problems in male automobile manufacturing workers
Suwhan Kim, Won-Ju Park, Seunghyeon Cho, Dae-Young Lim, Yeongjae Yoo, Hyeonjun Kim, Wonyang Kang, Kyung Wook Kang, Jai-Dong Moon
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association Between Long Working Hours and Infertility
Joonho Ahn, Sang Ha Lee, Min Young Park, Soo Hyun Oh, Wanhyung Lee
Safety and Health at Work.2021; 12(4): 517. CrossRef - Interaction between occupational physical burdens and low job control on musculoskeletal pain: Analysis of the 5th Korean Working Environment Survey
Jongin Lee, Hyoung-Ryoul Kim, Dong-Wook Lee, Mo-Yeol Kang
Journal of Occupational Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - PEMILIHAN ANALGESIK EKSTERNAL UNTUK MENGATASI NYERI OTOT PADA KULI ANGKUT PUSAT GROSIR SURABAYA
Nida Septioning Sukma, Devy Maulidya Cahyani, Yuniar Tri Saskia Revi, Evelyn Clarissa Febiany, Fatihatul Alifiyah, Berlian Sarasitha Hariawan, Iffah Khosyyatillah, Ni’matul Khoiriyyah, Savira Putri Ayuningtyas, Firda Rosyidah, Mufarrihah Mufarrihah
Jurnal Farmasi Komunitas.2020; 7(1): 23. CrossRef - Factors Related to Physical and Mental Health in Workers With Different Categories of Employment
Jungsun Park, Yangho Kim
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2020; 62(7): 511. CrossRef - Prevalence and predictors of work-related musculoskeletal disorders among workers of a gold mine in south Kivu, Democratic Republic of Congo
Alfred Okello, Solomon Tsebeni Wafula, Deogratias K. Sekimpi, Richard K. Mugambe
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Exposure to a Combination of Ergonomic Risk Factors with Musculoskeletal Symptoms in Korean Workers
Jungsun Park, Yangho Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9456. CrossRef - Prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal symptoms and associated risk factors among domestic gas workers and staff of works department in Enugu, Nigeria: a cross-sectional study
Chinenye Doris Oluka, Esther Obidike, Antoninus Obinna Ezeukwu, Ogochukwu Kelechi Onyeso, Echezona Nelson Dominic Ekechukwu
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to the risk of illness of nursing staff at work in a psychiatric institution
Kayo Henrique Jardel Feitosa Sousa, Regina Célia Gollner Zeitoune, Luciana Fernandes Portela, Gisele Massante Peixoto Tracera, Katerine Gonçalves Moraes, Rachel Ferreira Savary Figueiró
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Leisure time management in the workplace: Providing a model
Farkhondeh Forouzan, Hadi Teimouri, Ali Safari
Human Systems Management.2020; 39(3): 399. CrossRef - The association between long working hours and marital status change: middle-aged and educated Korean in 2014–2015
Hyunil Kim, Byung-Seong Suh, Won-Cheol Lee, Han-Seur Jeong, Kyung-Hun Son, Min-Woo Nam, Hyeong-Cheol Kim
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, patterns, and coping strategies of musculoskeletal disorders among caterers in the selected local government areas of Lagos State in Nigeria, 2017
Ashiyat Akodu, Ibitayo Famose
Journal of Occupational Health and Epidemiology.2019; 8(1): 29. CrossRef - The Effects of Workplace Rest Breaks on Health Problems Related to Long Working Hours and Shift Work among Male Apartment Janitors in Korea
Sungjin Park, June-Hee Lee, Wanhyung Lee
Safety and Health at Work.2019; 10(4): 512. CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Commuting time and musculoskeletal pain in the relationship with working time: a cross-sectional study
- Association between multiple jobs and physical and psychological symptoms among the Korean working population
- Association between single-person household wage workers in South Korea and insomnia symptoms: the 6th Korean Working Conditions Survey (KWCS)
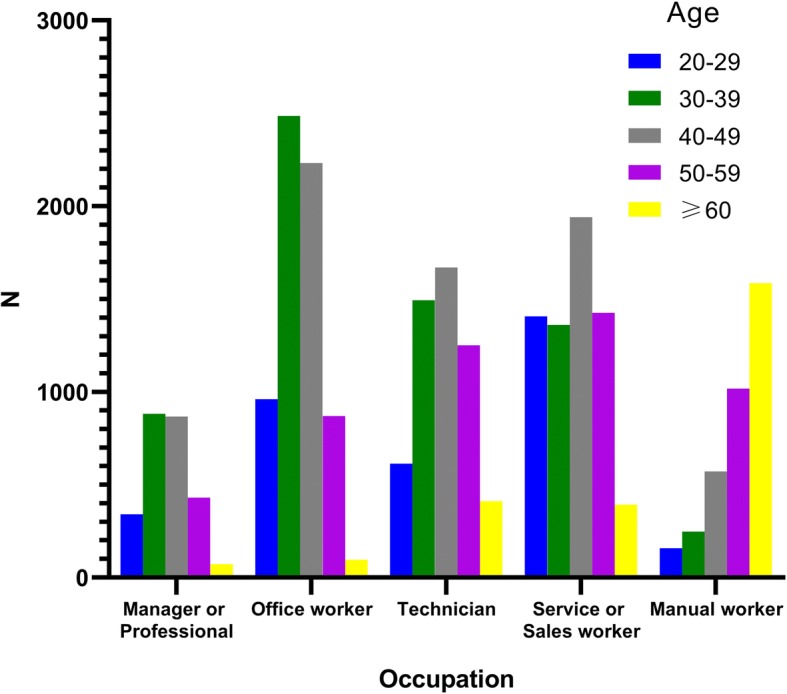
Fig. 1
| Characteristics | Total(N,%) | Weekly working hours | p-value* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤40 | 41-52 | > 52 | |||
| Total | 24,783(100) | 13,269(53.5) | 6956(28.1) | 4558(18.4) | |
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 11,890(48.0) | 6934(58.3) | 3182(26.8) | 1774(14.9) | < 0.001 |
| Male | 12,893(52.0) | 6335(49.1) | 3774(29.3) | 2784(21.6) | |
| Age (years) | |||||
| 20–29 | 3481(14.0) | 1841(52.9) | 990(28.4) | 650(18.7) | < 0.001 |
| 30–39 | 6469(26.1) | 3446(53.3) | 1977(30.6) | 1046(16.2) | |
| 40–49 | 7280(29.4) | 3959(54.4) | 2103(28.9) | 1218(16.7) | |
| 50–59 | 4995(20.2) | 2577(51.6) | 1386(27.7) | 1032(20.7) | |
| ≥ 60 | 2558(10.3) | 1446(56.5) | 500(19.5) | 612(23.9) | |
| Education | |||||
| Middle school graduate or below | 2659(10.7) | 1503(56.5) | 552(20.8) | 604(22.7) | < 0.001 |
| High school graduate | 9536(38.5) | 4354(45.7) | 2727(28.6) | 2455(25.7) | |
| College graduate or above | 12,588(50.8) | 7412(58.9) | 3677(29.2) | 1499(11.9) | |
| Monthly income (KRW) | |||||
| < 1,300,000 | 5478(22.1) | 3860(70.5) | 984(18.0) | 634(11.6) | < 0.001 |
| 1,300,000-1,999,000 | 6548(26.4) | 2747(42.0) | 2079(31.8) | 1722(26.3) | |
| 2,000,000-2,999,000 | 6964(28.1) | 3308(47.5) | 2282(32.8) | 1374(19.7) | |
| ≥ 3,000,000 | 5793(23.4) | 3354(57.9) | 1611(27.8) | 828(14.3) | |
| Occupation | |||||
| Managers or Professionals | 2594(10.5) | 1731(66.7) | 665(25.6) | 198(7.6) | < 0.001 |
| Office workers | 6644(26.8) | 4385(66.0) | 1858(28.0) | 401(6.0) | |
| Technicians | 5438(21.9) | 2279(41.9) | 1890(34.8) | 1269(23.3) | |
| Service or Sales workers | 6525(26.3) | 2877(44.1) | 1808(27.7) | 1840(23.7) | |
| Manual workers | 3582(14.5) | 1997(55.8) | 735(20.5) | 850(23.7) | |
| Employment status | |||||
| Regular | 18,754(75.7) | 9606(51.2) | 5729(30.5) | 3419(18.2) | < 0.001 |
| Temporary or Day labor | 6029(24.3) | 3663(60.8) | 1227(20.4) | 1139(18.9) | |
| Shift work | |||||
| No | 22,250(89.8) | 12,206(54.9) | 6242(28.1) | 3802(17.1) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 2533(10.2) | 1063(42.0) | 714(28.2) | 756(29.8) | |
| Number of employees | |||||
| < 50 | 18,082(73.0) | 9220(51.0) | 5149(28.5) | 3713(20.5) | < 0.001 |
| 50–299 | 4593(18.5) | 2734(59.5) | 1282(27.9) | 577(12.6) | |
| ≥ 300 | 2108(8.5) | 1315(62.4) | 525(24.9) | 268(12.7) | |
| Characteristics | Upper limb pain | p-value* | Lower limb pain | p-value* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No(%) | Yes(%) | No(%) | Yes(%) | |||
| Total | 9493(73.6) | 3400(26.4) | 10,782(83.6) | 2111(16.4) | ||
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 20–29 | 1356(84.6) | 246(15.4) | < 0.001 | 1461(91.2) | 141(8.8) | < 0.001 |
| 30–39 | 2813(77.8) | 804(22.2) | 3199(88.4) | 418(11.6) | ||
| 40–49 | 2623(73.2) | 960(26.8) | 3024(84.4) | 559(15.6) | ||
| 50–59 | 1734(66.5) | 872(33.5) | 2008(77.1) | 598(22.9) | ||
| ≥ 60 | 967(65.1) | 518(34.9) | 1090(73.4) | 395(26.6) | ||
| Education | ||||||
| Middle school graduate or below | 674(54.5) | 563(45.5) | < 0.001 | 797(64.4) | 440(35.6) | < 0.001 |
| High school graduate | 3153(67.9) | 1489(32.1) | 3684(79.4) | 958(20.6) | ||
| College graduate or above | 5666(80.8) | 1348(19.2) | 6301(89.9) | 713(10.2) | ||
| Monthly income (KRW) | ||||||
| < 1,300,000 | 1089(72.5) | 413(27.5) | < 0.001 | 1170(77.9) | 332(22.1) | < 0.001 |
| 1,300,000-1,999,000 | 1576(69.5) | 692(30.5) | 1790(78.9) | 478(21.1) | ||
| 2,000,000-2,999,000 | 3183(71.6) | 1261(28.4) | 3707(83.4) | 737(16.6) | ||
| ≥ 3,000,000 | 3645(77.9) | 1034(22.1) | 4115(87.9) | 564(12.1) | ||
| Occupation | ||||||
| Managers or Professionals | 1031(83.1) | 209(16.9) | < 0.001 | 1142(92.1) | 98(7.9) | < 0.001 |
| Office workers | 2981(84.7) | 537(15.3) | 3302(93.9) | 216(6.1) | ||
| Technicians | 2731(64.8) | 1486(35.2) | 3255(77.2) | 962(22.8) | ||
| Service or Sales workers | 1627(80.8) | 386(19.2) | 1752(87.0) | 261(13.0) | ||
| Manual workers | 1123(59.0) | 782(41.0) | 1331(69.9) | 574(30.1) | ||
| Employment status | ||||||
| Regular | 7874(75.7) | 2521(24.3) | < 0.001 | 8954(86.1) | 1441(13.9) | < 0.001 |
| Temporary or Day labor | 1619(64.8) | 879(35.2) | 1828(73.2) | 670(26.8) | ||
| Shift work | ||||||
| No | 8340(74.3) | 2890(25.7) | < 0.001 | 9475(84.4) | 1755(15.6) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 1153(69.3) | 510(30.7) | 1307(78.6) | 356(21.4) | ||
| Number of employees | ||||||
| < 50 | 6134(72.1) | 2375(27.9) | < 0.001 | 6976(82.0) | 1533(18.0) | < 0.001 |
| 50–299 | 2082(75.3) | 684(24.7) | 2373(85.8) | 393(14.2) | ||
| ≥ 300 | 1277(78.9) | 341(21.1) | 1433(88.6) | 185(11.4) | ||
| Working motion or posture | ||||||
| Lifting or carrying people | ||||||
| No | 5605(73.8) | 1990(26.2) | 0.054 | 6364(83.8) | 1231(16.2) | 0.192 |
| Yes | 3888(73.4) | 1410(26.6) | 4418(83.4) | 880(16.6) | ||
| Carrying heavy loads | ||||||
| No | 3215(84.0) | 614(16.0) | < 0.001 | 3503(91.5) | 326(8.5) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 6278(69.3) | 2786(30.7) | 7279(80.3) | 1785(19.7) | ||
| Standing continuously | ||||||
| No | 1935(84.1) | 365(15.9) | < 0.001 | 2093(91.0) | 207(9.0) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 7558(71.3) | 3035(28.7) | 8689(82.0) | 1904(18.0) | ||
| Repetitive movement | ||||||
| No | 1789(88.4) | 235(11.6) | < 0.001 | 1884(93.1) | 140(6.9) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 7704(70.9) | 3165(29.1) | 8898(81.9) | 1971(18.1) | ||
| Computer work | ||||||
| No | 2381(61.6) | 1484(38.4) | < 0.001 | 2817(72.9) | 1048(27.1) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 7112(78.8) | 1916(21.2) | 7965(88.2) | 1063(11.8) | ||
| Job stress | ||||||
| Low | 2307(76.4) | 713(23.6) | < 0.001 | 2550(84.4) | 470(15.6) | < 0.001 |
| High | 7115(72.8) | 2657(27.2) | 8150(83.4) | 1622(16.6) | ||
| No response | 71(70.3) | 30(29.7) | 82(81.2) | 19(18.8) | ||
| Social support | ||||||
| High | 8286(74.2) | 2877(25.8) | < 0.001 | 9435(84.5) | 1728(15.5) | < 0.001 |
| Low | 835(67.9) | 395(32.1) | 947(77.0) | 283(23.0) | ||
| No response | 372(74.4) | 128(25.6) | 400(80.0) | 100(20.0) | ||
| Characteristics | Upper limb pain | p-value* | Lower limb pain | p-value* | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No(%) | Yes(%) | No(%) | Yes(%) | |||
| Total | 7972(67.0) | 3918(33.0) | 9111(76.6) | 2779(23.4) | ||
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 20–29 | 1501(79.9) | 378(20.1) | < 0.001 | 1638(87.2) | 241(12.8) | < 0.001 |
| 30–39 | 2151(75.4) | 701(24.6) | 2428(85.1) | 424(14.9) | ||
| 40–49 | 2484(67.2) | 1213(32.8) | 2856(77.3) | 841(22.7) | ||
| 50–59 | 1320(55.3) | 1069(44.7) | 1603(67.1) | 786(32.9) | ||
| ≥ 60 | 516(48.1) | 557(51.9) | 586(54.6) | 487(45.4) | ||
| Education | ||||||
| Middle school graduate or below | 636(44.7) | 786(55.3) | < 0.001 | 750(52.7) | 672(47.3) | < 0.001 |
| High school graduate | 3073(62.8) | 1821(37.2) | 3588(73.3) | 1306(26.7) | ||
| College graduate or above | 4263(76.5) | 1311(23.5) | 4773(85.6) | 801(14.4) | ||
| Monthly income (KRW) | ||||||
| < 1,300,000 | 2422(60.9) | 1554(39.1) | < 0.001 | 2789(70.1) | 1187(29.9) | < 0.001 |
| 1,300,000-1,999,000 | 2859(66.8) | 1421(33.2) | 3249(75.9) | 1031(24.1) | ||
| 2,000,000-2,999,000 | 1856(73.7) | 664(26.3) | 2130(84.5) | 390(15.5) | ||
| ≥ 3,000,000 | 835(75.0) | 279(25.0) | 943(84.6) | 171(15.4) | ||
| Occupation | ||||||
| Managers or Professionals | 1016(75.0) | 338(25.0) | < 0.001 | 1123(82.9) | 231(17.1) | < 0.001 |
| Office workers | 2471(79.0) | 655(21.0) | 2860(91.5) | 266(8.5) | ||
| Technicians | 776(63.6) | 445(36.4) | 944(77.3) | 277(22.7) | ||
| Service or Sales workers | 2908(64.5) | 1604(35.5) | 3194(70.8) | 1318(29.2) | ||
| Manual workers | 801(47.8) | 876(52.2) | 990(59.0) | 687(41.0) | ||
| Employment status | ||||||
| Regular | 5743(68.7) | 2616(31.3) | < 0.001 | 6624(79.2) | 1735(20.8) | < 0.001 |
| Temporary or Day labor | 2229(63.1) | 1302(36.9) | 2487(70.4) | 1044(29.6) | ||
| Shift work | ||||||
| No | 7444(67.5) | 3576(32.5) | < 0.001 | 8512(77.2) | 2508(22.8) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 528(60.7) | 342(39.3) | 599(68.9) | 271(31.1) | ||
| Number of employees | ||||||
| < 50 | 6330(66.1) | 3243(33.9) | < 0.001 | 7259(75.8) | 2314(24.2) | < 0.001 |
| 50–299 | 1281(70.1) | 546(29.9) | 1452(79.5) | 375(20.5) | ||
| ≥ 300 | 361(73.7) | 129(26.3) | 400(81.6) | 90(18.4) | ||
| Working motion or posture | ||||||
| Lifting or carrying people | ||||||
| No | 4540(67.7) | 2164(32.3) | 0.054 | 5451(76.9) | 1550(23.1) | 0.192 |
| Yes | 3432(66.2) | 1754(33.8) | 3957(76.3) | 1229(23.7) | ||
| Carrying heavy loads | ||||||
| No | 3076(76.8) | 929(23.2) | < 0.001 | 3440(85.9) | 565(14.1) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 4896(32.1) | 2989(37.9) | 819(79.1) | 2155(20.9) | ||
| Standing continuously | ||||||
| No | 1575(77.1) | 468(22.9) | < 0.001 | 1809(88.5) | 234(11.5) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 6397(65.0) | 3450(35.0) | 7302(74.2) | 2545(25.8) | ||
| Repetitive movement | ||||||
| No | 1370(82.1) | 299(17.9) | < 0.001 | 1467(87.9) | 202(12.1) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 6602(64.6) | 3619(35.4) | 7644(74.8) | 2577(25.2) | ||
| Computer work | ||||||
| No | 1962(53.5) | 1706(46.5) | < 0.001 | 2333(63.6) | 1335(36.4) | < 0.001 |
| Yes | 6010(73.1) | 2212(26.9) | 6778(84.4) | 1444(17.6) | ||
| Job stress | ||||||
| Low | 2130(69.7) | 926(30.3) | 0.001 | 2393(78.3) | 663(21.7) | 0.039 |
| High | 5773(66.2) | 2950(33.8) | 6634(76.1) | 2089(23.9) | ||
| No response | 69(62.2) | 42(37.8) | 84(75.7) | 27(24.3) | ||
| Social support | ||||||
| High | 6650(67.6) | 3191(32.4) | 0.028 | 7643(77.7) | 2198(22.3) | < 0.001 |
| Low | 842(64.5) | 463(35.5) | 931(71.3) | 374(28.7) | ||
| No response | 480(64.5) | 264(35.5) | 537(72.2) | 207(27.8) | ||
| Weekly working hour | Upper limb pain | Lower limb pain | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | ||||||
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | ||
| Crude | ≤40 | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference |
| 41–52 | 1.50 | 1.37–1.65 | 1.22 | 1.16–1.33 | 1.39 | 1.24–1.55 | 1.17 | 1.06–1.29 | |
| > 52 | 1.90 | 1.73–2.10 | 1.96 | 1.76–2.18 | 2.09 | 1.87–2.34 | 1.98 | 1.77–2.22 | |
| Model I* | ≤40 | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference |
| 41–52 | 1.37 | 1.24–1.51 | 1.28 | 1.16–1.41 | 1.27 | 1.13–1.43 | 1.23 | 1.10–1.38 | |
| > 52 | 1.47 | 1.32–1.64 | 1.77 | 1.57–2.00 | 1.52 | 1.34–1.73 | 1.56 | 1.40–1.72 | |
| Model II** | ≤40 | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference |
| 41–52 | 1.36 | 1.23–1.50 | 1.26 | 1.14–1.39 | 1.26 | 1.11–1.42 | 1.20 | 1.07–1.35 | |
| > 52 | 1.40 | 1.25–1.57 | 1.66 | 1.46–1.89 | 1.47 | 1.29–1.68 | 1.47 | 1.28–1.69 | |
*calculated by chi-square test
*calculated by chi-square test
*calculated by chi-square test
*Adjusted for gender, age, education, occupation, monthly income, employment status, shift work and number of employees
**Adjusted for gender, age, education, occupation, monthly income, employment status, shift work, number of employees, working motion or posture, job stress, and social support
 KSOEM
KSOEM

 Cite
Cite

