Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Ann Occup Environ Med > Volume 30; 2018 > Article
- Case Report Acute radiation syndrome in a non-destructive testing worker: a case report
- Ji-Sung Ahn, Jai-Dong Moon, Wonyang Kang, Hyeong-Min Lim, Seunghyeon Cho, Dae-Young Lim, Won-Ju Park
-
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 2018;30:59.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40557-018-0270-8
Published online: September 25, 2018
Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, 322 Seoyang-ro, Hwasun-gun, Gwangju, Jeollanam-do 58128 Republic of Korea
© The Author(s). 2018
Open AccessThis article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Abstract
-
Background In Korea, there were repeated radiation exposure accidents among non-destructive testing workers. Most of the cases involved local injury, such as radiation burns or hematopoietic cancer. Herein, we report a case of acute radiation syndrome caused by short periods of high exposure to ionizing radiation.
-
Case presentation In January 2017, Korea Information System on Occupational Exposure (KISOE) found that a 31-year-old man who had worked in a non-destructive testing company had been overexposed to radiation. The patient complained of symptoms of anorexia, general weakness, prostration, and mild dizziness for several days. He was anemic. The venous injection areas had bruises and bleeding tendency. Blood and bone marrow testing showed pancytopenia and the patient was diagnosed with acute radiation syndrome (white blood cells: 1400/cubic mm, hemoglobin: 7.1 g/dL, platelets: 14000/cubic mm). He was immediately prohibited from working and blood transfusion was commenced. The patient’s radiation exposure dose was over 1.4 Gy (95% confidence limits: 1.1–1.6) in lymphocyte depletion kinetics. It was revealed that the patient had been performing non-destructive tests without radiation shielding when working in high places of the large pipe surface.
-
Conclusions Exposure prevention is clearly possible in radiation-exposed workers. Strict legal amendments to safety procedures are essential to prevent repeated radiation exposure accidents.
Background
| Yeara | Sex | Disease | Age at diagnosis (years) | Working duration (years) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Male | Acute radiation syndrome: pancytopenia, anemia | 31 | 5 | This study |
| 2015 | – | Radiodermatitis: ulcer at fingers | – | – | KINS [1] |
| 2013 | Male | Azoospermia | 39 | 8 | Park J, et al. [6] |
| 2010 | Male | Myelodysplastic syndrome | 35 | 9 | Oh MS, et al. [4] |
| 2009 | Male | Myelodysplastic syndrome | 26 | 1 | Oh MS, et al. [4] |
| 2004 | – | Radiodermatitis: necrosis at hand | – | – | KINS [11] |
| 2003 | – | Radiodermatitis: sclerosis at dorsum manus | 25 | – | KINS [11] |
| ~ 2000 | Male | Radiodermatitis: sclerosis at fingers | 40 | 10 | Park SW, et al. [10] |
| ~ 2000 | Male | Radiodermatitis: necrosis at palm | 32 | – | Park SW, et al. [10] |
| 1999 | – | Radiodermatitis: ulcer at fingers and palm | – | – | KINS [11] |
|
1986~ 1996 |
Male | Radiodermatitis: ulcer at fingers | 22 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: ulcer at fingers | 28 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: edema, erythema at fingers | 25 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: erosion at palm | 19 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: ulcer, sclerosis at fingers | 20 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: ulcer, sclerosis at palm | 21 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| ~ 1990 | Male | Radiodermatitis: desquamation, sclerosis at fingers | 22 | – | Ro YS [9] |
| 1989 | – | Amputation at fingers | – | – | KINS [11] |
| ~ 1989 | Male | Radiodermatitis: desquamation, sclerosis at fingers | 22 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [8] |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: hardening at fingers | 28 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [8] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: hardening at fingers | 25 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [8] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: edema at palm | 19 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [8] | |
| 1984 | Male | Radiodermatitis: soft tissue injury at palm | 29 | 1 | Yoon SC, et al. [7] |
| 1983 | Male | Radiodermatitis: elliptical ulcer at lower abdomen | 29 | 2 | Yoon SC, et al. [7] |
| 1983 | Male | Radiodermatitis: edema, amputation at finger | 19 | 0.1 | Yoon SC, et al. [7] |
Case presentation
Discussion
Conclusions
Abbreviations
ALC
AMC
ANC
WBC
- 1. http://www.kins.re.kr/.
- 2. Jin YW, Jeong M, Moon K, Jo MH, Kang SK. Ionizing radiation-induced diseases in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2010;25(Suppl):S70–S76. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.S.S70. 21258594.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Kim EA, Lee WJ, Son M, Kang SK. Occupational lymphohematopoietic cancer in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2010;25(Suppl):S99–104. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.S.S99. 21258598.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Oh MS, Yoon JK, Kim HS, Kim H, Lee JK, Lee JH, et al. Two cases of erythroleukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome in a non-destructive inspector. Korean J Occup Med. 2011;23:471–479.
- 5. Kim KJ, Yoo JH. Radiodermatitis from occupational exposure to 192 iridium. Korean J Occup Med 1998;10:128–135.
- 6. Park J, Lee S, Park C, Eom H. A case of azoospermia in a non-destructive testing worker exposed to radiation. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2017;29:33. 10.1186/s40557-017-0190-z. 28815050.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Yoon SC, Bahk YW, Shinn KS, Kim CY, Cho BK, Wee SS. Radiation dermatitis: report of 3 cases. J Korean Radiol Soc 1986;22:167–174. 10.3348/jkrs.1986.22.1.167.ArticlePDF
- 8. Kim KJ, Lee BK, Kanh HJ. Occupational radiodermatitis: report of 4 cases. Korean J Dermatol. 1989;27:686–690.
- 9. Ro YS. Occupational radiodermatitis due to Ir-192 exposure. J Hanyang Med Coll 1990;10:787–790.
- 10. Park SW, Kim JW, Hwang SW, Wang HY. Two cases of occupational radiodermatitis. Korean J Dermatol 2000;38:1409–1411.
- 11. http://www.kins.re.kr/nsic.do?menu_item=library/magine/reg_glossary.
- 12. http://www.nssc.go.kr/nssc/information/dataroom.jsp?mode=view&article_no=41968&pager.offset=0&search:search_key:search=article_title&search:search_val:search=%25B9%25E6%25BB%25E7%25BC%25B1&board_no=7.
- 13. Kim EA, Lee EJ, Kang SK, Jeong MS. Probability of causation for occupational cancer after exposure to ionizing radiation. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2018;30:3. 10.1186/s40557-018-0220-5. 29435338.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Seo SW, Lee DN, Seong KM, Park SH, Kim SG, Won JU, et al. Radiation-related occupational cancer and its recognition criteria in South Korea. Ann Occup Environ Med 2018;30:9. 10.1186/s40557-018-0219-y. 29435340.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Lichty PD. In: LaDou J, editor. Injuries caused by physical hazards. Current occupational & environmental medicine. 2014, 5. New York: McGraw-Hill; 187–188.
- 16. http://www.nssc.go.kr/nssc/notice/report.jsp?mode=view&article_no=43380&pager.offset=0&board_no=2.
- 17. Waselenko JK, MacVittie TJ, Blakely WF, Pesik N, Wiley AL, Dickerson WE, et al. Medical management of the acute radiation syndrome: recommendations of the strategic National Stockpile Radiation Working Group. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:1037–1051. 10.7326/0003-4819-140-12-200406150-00015. 15197022.ArticlePubMed
- 18. https://www.remm.nlm.gov/ars_wbd.htm.
- 19. Sarin R. Chernobyl, Fukushima, and beyond: a health safety perspective. J Cancer Res Ther 2011;7:109–111. 10.4103/0973-1482.82908. 21768693.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Brandao-Mello CE, Oliveira AR, Valverde NJ, Farina R, Cordeiro JM. Clinical and hematological aspects of 137Cs: the Goiania radiation accident. Healthy Phys 1991;60:31–39. 10.1097/00004032-199101000-00004.
- 21. Anjos RM, Umisedo NK, Facure A, Yoshimura EM, Gomes PR, Okuno E. Goiania: 12 years after the 137Cs radiological accident. Radiat Prot Dosim 2002;101:201–204. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a005967.
REFERENCES
Notes
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Computational retrospective dosimetry with fortuitous dosimeters: An inter-laboratory comparison and evaluation of dose conversion coefficients
Min Chae Kim, Hyoungtaek Kim, Yoomi Choi, Sora Kim, Jungil Lee, Byung Il Min, Kyungsuk Suh, Jiyoon Kim, Hanjin Lee, Jeong Tae Lee, Hyungjoon Yu, Young-su Kim, Han Sung Kim, Chan Hyeong Kim
Nuclear Engineering and Technology.2026; 58(5): 104152. CrossRef - Reference dosimetry for inter-laboratory comparison on retrospective dosimetry techniques in realistic field irradiation experiment using 192Ir
Yoomi Choi, Hyoungtaek Kim, Min Chae Kim, Hyungjoon Yu, Hyunseok Lee, Jeong Tae Lee, Hanjin Lee, Young-su Kim, Han Sung Kim, Jungil Lee
Nuclear Engineering and Technology.2022; 54(7): 2599. CrossRef - A small-scale realistic inter-laboratory accident dosimetry comparison using the TL/OSL from mobile phone components
Hyoungtaek Kim, Hyungjoon Yu, Michael Discher, Min Chae Kim, Yoomi Choi, Hyunseok Lee, Jeong Tae Lee, Hanjin Lee, Young-su Kim, Han Sung Kim, Jungil Lee
Radiation Measurements.2022; 150: 106696. CrossRef - Chromosome aberration dynamics in breast cancer patients treated with radiotherapy: Implications for radiation biodosimetry
Younghyun Lee, Jin-Kyu Kang, Yang Hee Lee, Hyo Jin Yoon, Su San Yang, Seung Hyun Kim, Seongjae Jang, Sunhoo Park, Da Hye Heo, Won Il Jang, Hyung Jun Yoo, Eun Kyung Paik, Hyo Rak Lee, Ki Moon Seong
Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis.2021; 872: 503419. CrossRef - Assessment of working environment and personal dosimeter-wearing
compliance of industrial radiographers based on chromosome aberration
frequencies
Younghyun Lee, Songwon Seo, Young Woo Jin, Seongjae Jang
Journal of Radiological Protection.2020; 40(1): 151. CrossRef
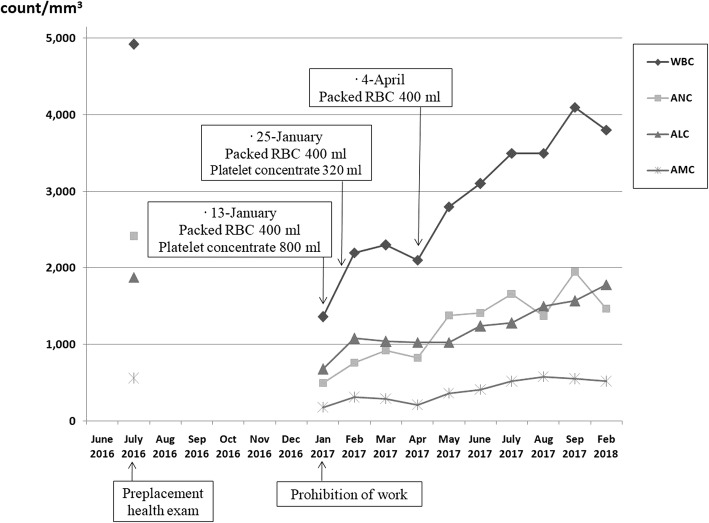
Fig. 1
| Yeara | Sex | Disease | Age at diagnosis (years) | Working duration (years) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Male | Acute radiation syndrome: pancytopenia, anemia | 31 | 5 | This study |
| 2015 | – | Radiodermatitis: ulcer at fingers | – | – | KINS [1] |
| 2013 | Male | Azoospermia | 39 | 8 | Park J, et al. [6] |
| 2010 | Male | Myelodysplastic syndrome | 35 | 9 | Oh MS, et al. [4] |
| 2009 | Male | Myelodysplastic syndrome | 26 | 1 | Oh MS, et al. [4] |
| 2004 | – | Radiodermatitis: necrosis at hand | – | – | KINS [11] |
| 2003 | – | Radiodermatitis: sclerosis at dorsum manus | 25 | – | KINS [11] |
| ~ 2000 | Male | Radiodermatitis: sclerosis at fingers | 40 | 10 | Park SW, et al. [10] |
| ~ 2000 | Male | Radiodermatitis: necrosis at palm | 32 | – | Park SW, et al. [10] |
| 1999 | – | Radiodermatitis: ulcer at fingers and palm | – | – | KINS [11] |
| 1986~ 1996 | Male | Radiodermatitis: ulcer at fingers | 22 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: ulcer at fingers | 28 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: edema, erythema at fingers | 25 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: erosion at palm | 19 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: ulcer, sclerosis at fingers | 20 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: ulcer, sclerosis at palm | 21 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [5] | |
| ~ 1990 | Male | Radiodermatitis: desquamation, sclerosis at fingers | 22 | – | Ro YS [9] |
| 1989 | – | Amputation at fingers | – | – | KINS [11] |
| ~ 1989 | Male | Radiodermatitis: desquamation, sclerosis at fingers | 22 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [8] |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: hardening at fingers | 28 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [8] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: hardening at fingers | 25 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [8] | |
| Male | Radiodermatitis: edema at palm | 19 | – | Kim KJ, et al. [8] | |
| 1984 | Male | Radiodermatitis: soft tissue injury at palm | 29 | 1 | Yoon SC, et al. [7] |
| 1983 | Male | Radiodermatitis: elliptical ulcer at lower abdomen | 29 | 2 | Yoon SC, et al. [7] |
| 1983 | Male | Radiodermatitis: edema, amputation at finger | 19 | 0.1 | Yoon SC, et al. [7] |
| Variables | Normal ranges | Preplacement medical exama | Days after prohibition of work | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 26 | 82 | 119 | 174 | 256 | 405 | |||
| WBC (count/mm3) | 4000-10,800 | 4920 | 1360 | 1400 | 2200 | 2100 | 2800 | 3500 | 4100 | 3800 |
| ANC (count/mm3) | 1500-8000 | 2410 | 500 | 590 | 760 | 830 | 1380 | 1660 | 1950 | 1470 |
| ALC (count/mm3) | 1500-4000 | 1880 | 680 | 650 | 1080 | 1030 | 1030 | 1280 | 1570 | 1780 |
| AMC (count/mm3) | 200–1000 | 560 | 179 | 150 | 310 | 210 | 360 | 520 | 550 | 520 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 12–18 | 14.7 | 7.5 | 7.1 | 10.3 | 7.3 | 10.8 | 13.2 | 14.0 | 14.1 |
| RBC (× 103/mm3) | 420–610 | 458 | 201 | 293 | 191 | 284 | 370 | 407 | 419 | |
| Hematocrit (%) | 37–52 | 44.4 | 19.4 | 28.9 | 20.7 | 31.3 | 38.8 | 41.4 | 42.8 | |
| Platelet (× 103/mm3) | 130–450 | 217 | 14 | 27 | 38 | 51 | 130 | 101 | 115 | |
| Reticulocyte (%) | 0.5–1.5 | 1.05 | 1.72 | 1.69 | 1.9 | 1.54 | ||||
aYear of diagnosis
aThe preplacement medical examination was conducted 6 months prior to the accident
 KSOEM
KSOEM

 Cite
Cite

