Establishment and operation of a cooperative program to identify work-related acute myeloid leukemia in a general hospital
Article information
Abstract
Background
The purpose of this report is to introduce the occupational cancer surveillance system, implemented in June 2018, and to share the results of our cooperative program.
Methods
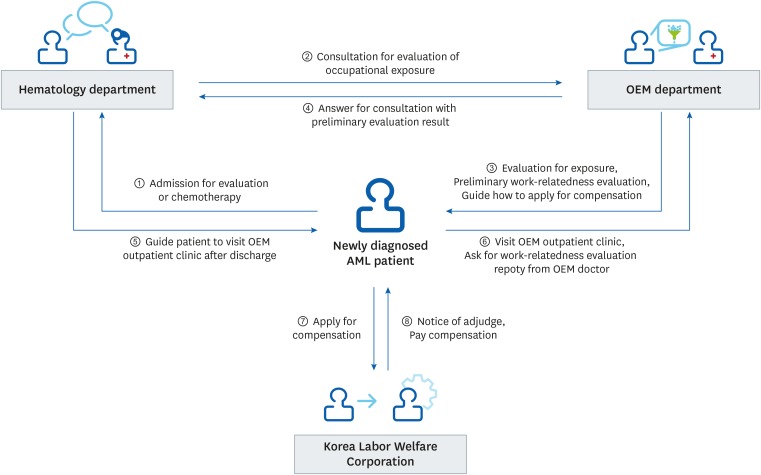
The cooperative program begins when the patient is diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Newly diagnosed AML patients are admitted to the internal medicine hematology department, then attending hematology physician requests a consultation from the occupational and environmental medicine (OEM) department. The OEM doctor next visits the hospitalized patient and interviews them to take their occupational history, and preliminarily evaluates the likelihood that the condition is associated with occupation. If the patient wants to apply for compensation through the Korea Workers' Compensation & Welfare Service, the patient was informed to visits the outpatient clinic of the OEM department and requests a ‘work-relatedness evaluation report’ for use in applying for compensation.
Results
Among the 103 patients, who received an OEM departmental work history evaluation, 18 patients were considered to have a work-related incidence and 12 patients were registered in the Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance system.
Conclusions
The present report provides data on a sustainable model for identifying occupational disease in a general hospital setting, while also informing patients about their occupational rights.
INTRODUCTION
Cancer is the leading cause of death in developed countries [1]. There were an estimated 17 million cancer diagnoses in 2018, excluding non-melanoma skin cancer, and 9.5 million cancer deaths worldwide [2]. Reports suggest that 3%–6% of all cancers worldwide are caused by exposures to carcinogens in the workplace [34]. In Korea, it has been reported that the rate of cancer diagnosis attributable to occupational exposure is 9.3% of the total cancer diagnosis rate [5]. Therefore, understanding the extent to which occupational exposure contributes to overall cancer risk is an important issue in occupational health and safety.
Lymphohematopoietic (LHP) cancer accounts for 3.5% of the overall cancer incidence and 3.8% of cancer mortality. Worldwide, the incidence of occupational-related leukemia (a form of LHP) is 2% of the population attributable fraction (PAF), as reported in a study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO) [36]. In Korea, the age-standardized registration rate of LHP cancer is 6.2 per 100,000 and the occupation-attributable fraction of leukemia is estimated at 14.93% [5]. From 2010 to 2018, the Korea Workers' Compensation & Welfare Service (KCOMWEL) received 1,852 applications for compensation for occupational cancer, and of which 838 cases (45.2%) were approved. Occupational cancer insurance claims approved by the Occupational Compensation Insurance Act have been gradually increasing, including in those with LHP cancer. In the year 2017, the proportion of approved applications was 61% (164 of the 268 applications were approved), and most of these cases were due to respiratory cancer (133 respiratory cancer cases were approved of the 171 applications) [7]. Although LHP cancer is the second most common occupational cancer following respiratory cancer in Korea [5], only 32 patients with LHP cancer applied for compensation, and only 13 patients were approved. The primary reasons why employees may not apply for compensation include being unaware of both the occupational compensation system and the possibility their condition could be work-related.
The purpose of the industrial accident compensation insurance system in domestic law is to compensate workers for work-related accidents and disease, ultimately to protect workers from suffering severe financial hardship. Appropriate compensation for patients with occupationally associated disease, especially cancer, is important because patients inevitably experience an inability to work and have persistent life-long health concerns. For that object, the present study reports on the establishment of an occupational LHP cancer cooperation program between a hematology department and an occupational and environmental medicine (OEM) department in general hospital setting. The fundamental purpose of this program was introducing caregivers and patients with occupationally originated LHP cancer to the compensation system and evaluating the relationship between their condition and their prior or current employment. This program is targeting acute myeloid leukemia (AML) as a pilot, since the association between AML and occupational exposure is relatively well known [8910111213].
In addition to this fundamental purpose, the cooperation program between the hematology and OEM departments also plays a role in the occupational cancer surveillance system. To prevent the health risks to workers from these hazardous environments, occupational diseases that are missing from official statistics also should be revealed. In addition, occupational health programs should be able to prevent the occurrence of diseases through feedback to other workplaces within similar industries and those involving similar hazardous work environments. This will require the establishment of an effective surveillance system to identify and connect occupational health service agencies, medical institutions, health institutions, and clinical medical experts in the associated diseases and conditions.
Through ongoing monitoring of this surveillance system, we will be able to identify the incidence of hidden occupational AML and provide basic data for estimation of the size of the occupational LHP population in Korea. We expected the current cooperative system to establish baseline data for the identification of high-risk groups and preventing occupational LHP cancer. The purpose of this report is to introduce the occupational cancer surveillance system, implemented in June 2018, and to share the results of our cooperative program.
METHODS
Cooperative program design
The cooperative program begins when the patient is diagnosed with AML (Fig. 1). Newly diagnosed AML patients are admitted to the internal medicine hematology department for evaluation and treatment. The attending hematology physician requests a consultation from the OEM department upon hospital admission. The OEM doctor next visits the hospitalized patient and interviews them to take their occupational history. The OEM practitioner preliminarily evaluates the likelihood that the disease is related to patient's occupational history on the basis of the exposure level to hazardous materials, exposure time, latency period, and other factors. The patient whose likelihood of work-related incidence is higher than “possible” (see “Work-relatedness evaluation”), the OEM practitioner informs the patient about work-related hematologic disease and the way for compensation under the Industrial Accident Compensation and Insurance Act and provides a brochure. The patient is guided to visit the outpatient clinic of OEM department if the patient wants to apply for compensation through the KCOMWEL After that the patient visits the outpatient clinic of the OEM department and requests a ‘work-relatedness evaluation report’ for use in applying for compensation.
Disease entry
Disease entry was constructed according to AML diagnostic criteria and classified by the Korean Standard Classification of Diseases (KCD-7) diagnosis code: C9201, C9208, C9209, C924, and C925. Inpatients who were subject to this surveillance program were admitted for further evaluation and chemotherapy after bone marrow biopsy at the outpatient clinic. Patients whose final diagnosis was an alternate disease, such as myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), were excluded from this report even if they were suspected to have AML via bone marrow biopsy at the beginning of examination.
Patient population
Patients who were hospitalized for the first time in the hematology department were asked to consult with the OEM department to take work history evaluation. Consultation between the hematology department and the OEM department on work history and occupational disease evaluation began on June 1, 2018. Only patients aged 19 years or older were referred for evaluation of occupational exposure. In this study, the result of consultation from June 1, 2018 to December 31, 2018 were included.
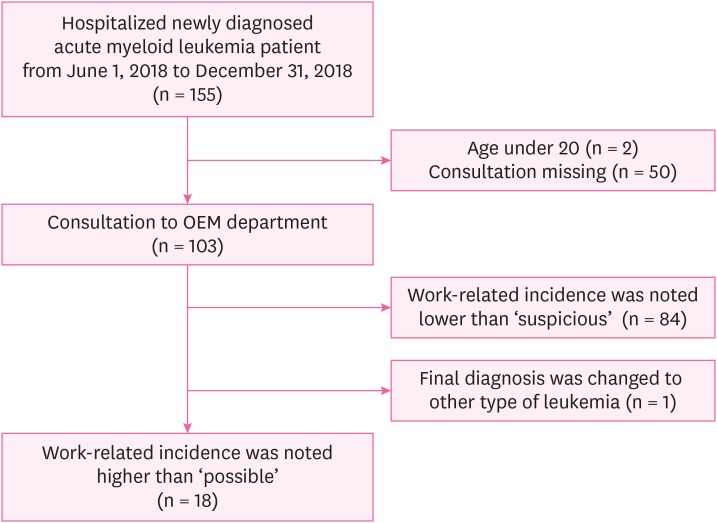
Out of the 155 newly diagnosed AML patients who were admitted to the hematology department, 2 were excluded because they were under 20 years, and 50 were excluded because OEM departmental consultation was not requested. Among the 103 patients who received an OEM departmental work history evaluation, one was excluded because his final diagnosis was changed from AML to MDS. Of this cohort, it was determined that 18 patients were eligible for work-related compensation (Fig. 2). The Institutional Review Board at The Catholic University of Korea approved publication of this program (IRB approval number: KC19RESI0016).
Work-relatedness evaluation
Three trained OEM practitioners administered structured occupation and exposure questionnaires to the AML patients. Detailed occupational history taking was accompanied by medical history taking.
From the questionnaire, researchers identified occupational exposure to hazardous substances and processes according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) monograph for myeloid leukemia. A report implementing a benzene job-exposure matrix, a reference identifying criteria for occupational cancer, and an occupational disease assessment manual were also used as a reference for the questionnaire, among other sources [5101112131415161718]. We categorized the work relatedness of the condition into “definite”, “probable”, “possible”, and “suspicious” based on the exposure intensity, exposure time, and latency period of the hazardous work environment. Exposure was evaluated with combination of grading hazardous level according to IARC group (B), exposure period (C), exposure level (D) with combination of duration (E), intensity (F). Considering latent period (G), if participants had been exposed less than 1 year, evaluator took one grade down for work-relatedness. Hazardous level of substance (B) is decided by IARC group, IARC group1 is B1, group 2A is B2 while exposed period (C) is divided into C1 (exposed to hazard substance for 10 years and more) and C2 (exposed to hazard substance for less than 10 years). Aggregating these indexes, researchers assessed the preliminary work-relatedness. Patients who were evaluated as “possible”, “probable”, “definite" in preliminary evaluation were considered as work-related incidence cases.
Statistical analysis
We summarized descriptive characteristics of patients who were consulted by the OEM department and who presented with AML associated with occupational exposure. Participant characteristics were calculated as means and percentages. Differences in these characteristics between the two groups of newly diagnosed AML patients, with or without consultation to OEM department, were tested separately using a t-test and χ2 test.
RESULTS
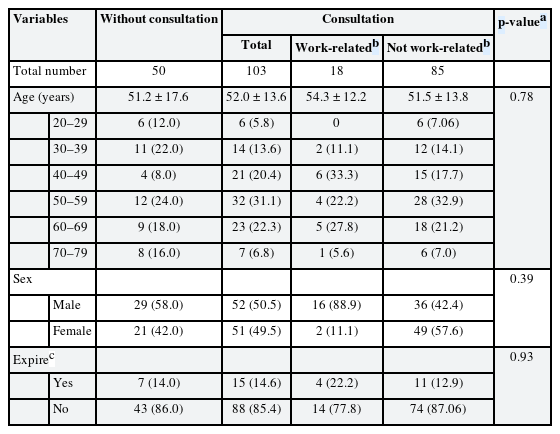
Table 1 presents the socio-demographic characteristics of participants by the total number of newly diagnosed AML patients and those in the OEM consulted group. There were no statistically significant characteristic differences between the consulted group and non-consulted group. In the consulted group, those with a “possible” to “probable” work-related condition were further categorized as the “work-related group”, as seen in Table 1. Categorical values are presented with the number of participants, followed by percentage in brackets. The mean age of the total participants, the consulted group, and work-related group are presented with standard deviation following the ± mark. Detailed characteristics of the work-related group are summarized in Table 2. Initially there were 19 AML patients who were considered to have a work-related incidence. However, one patient was later diagnosed with MDS and subsequently excluded. In the work-related group, 8 patients received a “possible” rating, and 10 were given a “probable” rating as a result of the preliminary evaluation.
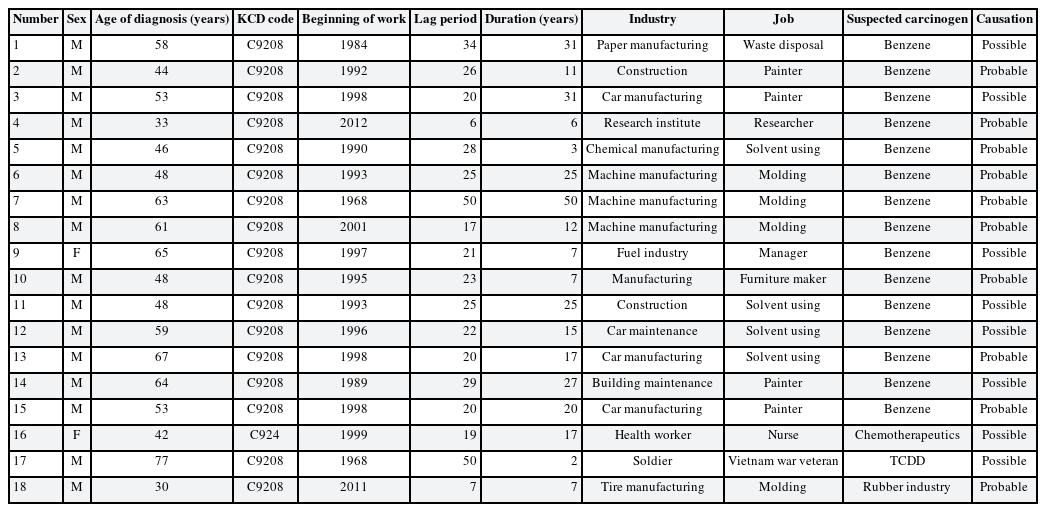
The characteristics of work-related AML patients among consultation requested to the department of OEM
The major hazardous substance was benzene. With the exception of one participant who worked in the waste disposal section of paper manufacturing, benzene was exposed in various work environments—an impurity in mixtures, such as in cement, solvents, cleaning agents, and hardeners.
There were only two female patients with work-related incidence. One had been a nurse for 17 years and had been exposed to chemotherapeutic agents. The other female patient was an owner of gas station and car repair shop, had been exposed by various solvent. There was a Vietnam war veteran who had been exposed to the toxic agent 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Two patients who worked in tire manufacturing were determined to have exposure as ‘rubber industry workers.’
The latency period was calculated based on when the exposure first began, and the mean value was 24.6 years, with a 6-year minimum. The mean working duration was 17.4 years and the minimum value was 2 years.
Among the 18 patients who were considered to have work-related AML patients, 12 of them were registered in the Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance system. Five patients visited the OEM outpatient clinic after they were discharged from the hospital and applied for compensation. The caregiver of the MDS diagnosed patient who was excluded from this study because of final diagnosis also visited the OEM outpatient clinic and applied for compensation. Patient No. 17, a Vietnam veteran, was victim of defoliant, guided by the Act to Support Veterans Suffering from Exposure to Defoliants.
Patients worked in various workplaces and were exposed to multiple hazardous materials, in addition to those reported in Table 2. For example, participant No. 9 had operated a gas station for 7 years starting in 1997 and performed the oil changes and oil delivery service. She also performed flat-tire patching at a car repair shop with unspecified glues, including rubber glue, from 1977 to 1997. In this case, working at car repair shops may also have contributed to the onset of LHP cancer through exposure to a variety of carcinogens.
DISCUSSION
The purpose of this program is 1) to identify the hidden incidence of occupational AML, 2) to inform patients and caregivers that occupational exposure can cause severe disease, and 3) to inform patients that compensation is available through KCOMWEL. At the same time, this study provided data for estimating the rates of occupationally associated LHP cancer, and identifying those at high occupational risk for the disease in Korea.
Of the total number of AML patients who consulted with the OEM department, 17.5% were determined to have work-related AML. Since myeloid leukemia is only the second most prevalent diagnosis of LHP cancer following non-Hodgkin lymphoma [14], the proportion of work-related incidences would likely be increased with the inclusion of other forms of cancer. However, previous studies found that the occupational attributable fraction of leukemia was only approximately 15% [5].
One of the strengths of the current report is that hidden work-related incidences of LHP cancer were revealed even when patients were not aware of work-relatedness. In previous studies of occupational LHP cancer in Korea, the study populations were limited to workers who had already applied for compensation from KCOMWEL, and analysis included approved cases only [71920]. Other studies were conducted to determine the cancer risk of workers in specific industries, and measured the exposure to hazardous materials that can cause LHP cancer [21222324]. Those studies were used to establish exposure limits and determine the causes of disease incidence. The current report applies these data to real patients, revealing incidence of hidden work-related LHP cancer. There also have been previous efforts to establish surveillance systems for work-related LHP cancer in Korea [252627282930]. The previous surveillance system was run in 2 ways: first, one was an outpatient-based method in which the OEM doctor collected the occupational history checklist of hematology department outpatients, and evaluated patient exposure on the phone. The second was an inpatient-based method in which the OEM doctor periodically received the list of hematology department inpatients, and recorded their occupational history when they were admitted. As a result, both methods were not able to provide feedback to the hematology department clinician who was in charge of patient care. One valuable result of our cooperative program is the establishment and operation of a sustainable surveillance system in a general hospital setting. This program is not a research project, but a program to evaluate a patient's occupational exposure history for clinical purposes. Furthermore, a reply from the OEM doctor informs the patient's clinical physician in the hematology department of the work-relatedness of the disease as feedback. Therefore, the clinical physician can also pay attention to the occupational exposure of the patient, and can contribute more actively to this cooperative program. This system helps patients recognize themselves as workers who were endangered by workplace hazards.
To help establish and eventually maintain a general occupational cancer surveillance system we first decided to start with a pilot study limited only to AML. After stabilization of the current consult system, we will consider expanding disease inclusion with the cooperation of other departments and institutions.
One major limitation of this study is recall bias. We attempted to reduce the effect of recall bias by careful assessment of the degree of hazardous substance exposure through detailed evaluation of the work processes and duties and work place environment of each patient. Exposure measurement data were also obtained from previous studies, and used as references when evaluating exposure grade. Another limitation of this study is that occupational exposure was not evaluated by actual workplace measurements but indirectly through the patient's statement and past exposure measurement data. This may result in low specificity of the preliminary evaluation. The preliminary evaluation tool should be updated continuously by tracking the approval results of patients who applied to the KCOMWEL. Moreover, this cooperative system inevitably requires close cooperation with the hematology department since this program starts with a consultation from the hematology department. Hematology doctors can obtain information about a patient's exposure on the reply letter from the OEM doctor, and draw attention to work-related diseases. Therefore, hematology doctors are more interested in occupational exposure and are willing to contribute to this cooperative system. Hematology doctors consulted only 7 cases (no AML case included) through the outpatient clinic within 5 months before the beginning of the cooperative program (from January 1, 2018 to May 31, 2018). They consulted 27 cases during the rest of the year, 9 of the cases being AML. As consultations through the outpatient clinic are not part of the cooperative program, increasing numbers of consultation from the hematology doctors imply that the program may have educative effects on work-related hematological diseases to the clinicians.
However, in this study, 50 patients missed their consultations, so we reviewed the medical records of these patients: 5 patients were in critical condition at the beginning of hospitalization, or expired within 48 hours of admission; diagnosis was changed within 48 hours of hospitalization in 4 cases; MDS, the secondary AML, developed after chemotherapy for solid cancer. Except for these cases, we found that the doctor who was in charge of most patients tended to miss the consultation. In order to operate the cooperative system more efficiently, it seems necessary to consult the request procedure to reduce the missing the consultation. Likewise, appropriate reward, such as high rating on hospital accreditation or reasonable medical insurance fee, will encourage clinical physicians to have concern about work-relatedness. Furthermore, consultation fee during admission is not from research fund or public resources since this system is a cooperative program. This is one of the concerned limitation of current cooperative system and it is necessary to establish fee for hazard exposure evaluation for the future.
CONCLUSION
The current report was result of program to identify work-related acute myeloid leukemia in a general hospital. We identified work-related AML patients from a general population of newly diagnosed patients who were referred to an OEM department from a hematology department. The present report provides data on a sustainable model for identifying occupational disease in a general hospital setting, while also informing patients about their occupational rights. The cooperative system is still evolving and will be developed and revised to include other conditions in the future.
Notes
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors contributions:
Conceptualization: Jung J, Choi HR, Kang MY, Cho BS, Kim HJ, Park S.
Data curation: Jung J, Choi HR.
Formal analysis: Jung J, Choi HR, Kang MY, Cho BS, Kim HJ, Park S.
Investigation: Jung J, Kang MY, Cho BS, Kim HJ, Park S.
Writing - original draft: Jung J.
Writing - review & editing: Jung J, Choi HR, Kang MY, Myong JP.
Abbreviations
AML
acute myeloid leukemia
IARC
International Agency for Research on Cancer
KCD-7
Korean Standard Classification of Diseases
KCOMWEL
Korea Workers' Compensation & Welfare Service
LHP
lymphohematopoietic
MDS
myelodysplastic syndrome
OEM
occupational and environmental medicine
PAF
population attributable fraction
TCDD
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
WHO
World Health Organization